What to Expect as Your Dog Ages
DOGS
22 Jul, 2020
READ 7 minutes

Your dog has been a loving, loyal companion for a long time. Now, you start to notice that as your dog is aging, he or she is not as active as before, or not quite as attentive. Perhaps he or she is sleeping a lot more lately, or having accidents in the house after years of being perfectly house-trained. Could it be that your beloved pet is growing old?
As inevitable as aging is for humans, dogs also grow old. Your dog’s needs are starting to change, but he or she still has a lot of life left in that furry body, and a lot of love as well. Your pet will depend on you to keep him or her healthy and comfortable during this phase of life.

SIGNS OF AGING IN YOUR DOG
For the most part, a dog is considered to reach “old age” at about seven years, although it differs slightly, depending on the breed and size of the dog. Larger dogs generally begin to age about a year or so earlier than smaller dogs, but as with humans, the extent of aging in dogs is also dependent on genetics, diet, exercise and overall health. Also similar to humans, dogs’ metabolism and immune systems slow down. They can get arthritis, vision impairment, and loss of bladder and bowel control.
Some visible signs of aging in your dog may include:
- Changes in physical appearance – such as graying fur around the muzzle and eyebrows. Also, your dog’s coat may look as though it has lost its luster and appear dull.
- Changes in activity level – your dog may be less active and eager to play than before, and sleeping more.
- Changes in disposition – your dog may be more irritable around children and other dogs.
- Other changes – including joint problems, hearing impairment, eyes tearing up and digestion issues.
HOW DO I CARE FOR MY AGING DOG’S HEALTH?
Your old friend should be examined by your veterinarian at least once a year, if not twice. The vet will be able to identify any age-related problems, check hearing and vision, as well as the liver and pancreas. Other tests can detect signs of heart disease.
Other diseases older dogs are prone to develop include:
- Osteoarthritis and other musculoskeletal disorders
- Diseases caused by hormonal changes, such as diabetes
- Dementia
- Dental problems
You will also want to make your aging pet as comfortable as possible. If yourx dog has joint pain, he or she may prefer resting on a pillow or blanket, rather than on the hard floor. If digestion problems are an issue, a change in diet may be required; and if your dog needs to go to the bathroom more frequently, he or she will need to be taken out more frequently.

HOW SHOULD I CARE FOR MY AGING DOG’S NUTRITION?
Your aging dog is most likely not moving as much as he or she used to. He or she also does not require as much food to maintain body weight, so it is important to adjust his or her diet accordingly. Your veterinarian will be able to recommend a senior diet which contains easily digestible nutrients and prevents obesity and gastrointestinal upsets. Older dogs are more prone to dehydration, so making sure there is always access to water is also an excellent idea.
It is particularly important to keep up grooming for your older dog. As his or her coat and skin start to become dry, regular brushing will help release natural oils and maintain some youthful luster. Regular grooming will also help you notice if your dog develops any lumps, tumors or other abnormalities. If you do notice anything unusual, you should let your vet know.
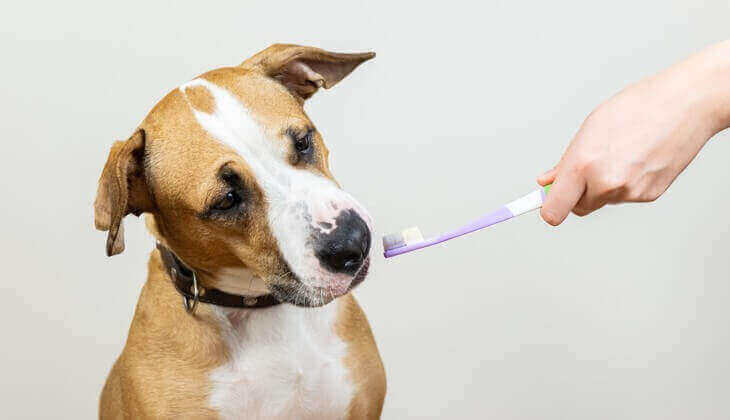
HOW SHOULD I CARE FOR MY AGING DOG’S TEETH AND GUMS?
The older your dog gets, the more you will need to pay attention to his or her teeth and gums. Dogs run a high risk of dental disease as they age and it is common for them to lose some teeth and develop bad breath. Keeping your dog’s teeth clean and tartar-free will help diminish the chances that serious problems will develop, such as heart disease, which can result from tooth decay.
HOW DO I KNOW IF MY DOG IS GOING DEAF OR BLIND?
It is common for dogs to lose their hearing as they age, just as humans do. If you notice that your dog is less responsive to your greetings or commands, he or she may have developed hearing problems. Your vet will be able to confirm the extent of the issue but you can learn to communicate with your pup through touch and hand signals. You should remember not to disturb your dog while he or she is sleeping and don’t approach him or her from behind.
Failing eye sight is also common in older dogs. Your dog’s eyes may appear cloudy, which could be an indication of vision problems. Again, your vet can confirm if this is an issue. To help your dog, you can maintain a consistent environment in your home. Avoid rearranging furniture or moving his or food bowls, toys or sleeping spot. This will confuse and frustrate your dog, causing stress that could worsen the condition.

HOW DO I SUPPORT MY SENIOR DOG IN EVERYDAY LIFE?
Many dogs suffer arthritis as they age and you may find that your dog is stiff and sore when he or she tries to get up, especially after a good long nap. Assistance may be required in climbing stairs, getting in and out of the car, and getting up on the sofa for cuddles with you. Your vet may recommend an anti-inflammatory to ease the pain for your four-legged friend, but you can also help out in a few ways, such as the following:
- Make sure your dog still gets daily exercise. This will benefit your beloved pet both physically and mentally.
- Keep nails trimmed short and put down rugs or non-skid mats on uncarpeted floors to reduce the risk of falls.
- Provide a soft resting place so those old bones and joints don’t have to lie on the hard floor.
- Give your old dog all the space and quiet he or she requires.
It is also helpful to stick to a routine for your aging dog. Taking walks at the same time every day and having a regular feeding time give your old dog a sense of security and comfort. Your dog may be getting older, but he or she is still the same one you brought into your home as a pup. He or she will still love playing the same games you played when he or she was younger, to the best of both of your abilities. He or she will still want your attention and affection because no matter how old your furry companion gets, his or her love for you will not diminish.
RECOMMENDED
RELATED POSTS
-

Learn about canine babesiosis, a tick-borne disease that affects dogs worldwide. Discover its symptoms, treatments, and how to prevent it.
-

Explore how diabetes impacts cats, its signs, risk factors, and effective management through medication and diet for a healthier feline life.
-

Diabetes affects an estimated 1 in 300 dogs, diabetes is more common in middle-aged and older dogs (4-14 years of age), it can be diagnosed in dogs of any age, including young dogs. Read more.
-

Ever wonder how your dog experiences the world? Why he or she sniffs everything, everywhere? Read more and find out






